Complete denture rehabilitation can improve oral health-related quality of life (OHRQoL) of patients. However,
some patients reported difficulties in performing daily activities caused by their denture. The aims of this review
article were to review the socio-dental indicators used for assessing OHRQoL of complete denture wearers and/or
edentulous people. In addition, the factors associated with OHRQoL of complete denture wearers were discussed,
including denture- and patient-related factors. The reviewed articles showed that denture retention and stability
are the most significant factors which affects OHRQoL of complete denture wearers. Optimal numbers of posterior
occlusal teeth which equally distribute on both left- and right-handed sides of the jaw enhance better masticatory
efficiency, and therefore, improve OHRQoL. Denture retention/stability tends to change faster in patients with flat- or
knife-edge residual ridge form, compared with those with round ridge. This review article provides information for
dentists when communicating to patients with regards to treatment limitations and possible post-insertion problems.
The review includes recommendations in patient evaluations before, during, and after treatment, even in long-term
follow-up. The ultimate goal is to achieve good oral health and quality of life among complete denture wearers.
JOURNAL OF THE DENTAL ASSOCIATION OF THAILAND
1
Page : 369-378Title : Oral Health-related Quality of Life of Complete Denture Wearers and Relating Factors
Author(s) : Nareudee Limpuangthip
Keyword(s) : Complete denture,Occlusion,Oral health-related quality of life,Masticatory efficiency,Retention,Stability
Manuscript Type : Review Article (บทความปริทัศน์)
Page : 369-378
2
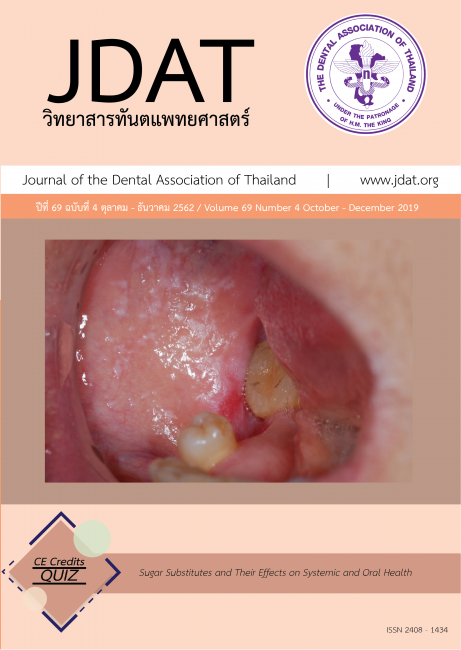
Page : 379-397Title : Sugar Substitutes and Their Effects on Systemic and Oral Health
Author(s) : Oranart Matangkasombut, Panida Thanyasrisung
Keyword(s) : Dental caries,Sugar substitutes,Sweeteners,Systemic health
Manuscript Type : Review Article (บทความปริทัศน์)
Page : 379-397
Sugar substitutes have become increasingly popular and are used in a wide variety of food and beverage
products in the current market. This is partly in response to consumers’ demands to reduce sugar intake in an effort
to reduce the risks of adverse effects on systemic and oral health due to sugar overconsumption. With regards
to systemic health, most consumers assume that the use of sugar substitutes would reduce the risks for several
important and increasingly prevalent chronic non-communicable diseases related to sugar overconsumption, such as,obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases. However, several lines of evidence from animal and longitudinal
cohort studies suggested that long-term consumption of sugar substitutes may not be able to reduce the risks for
these diseases as expected. Numerous mechanisms have been discovered that could explain how sugar substitutes
could affect metabolism and physiology. Interestingly, they may induce changes in gut microbiota, which are now
known to influence nutrient absorption, metabolism, and the functions of other organ systems. With regards to
oral health, sugar substitutes are widely used to reduce cariogenicity of sweet food and beverages since they are
not good substrates for cariogenic bacteria. In addition, certain sweeteners may be useful as an adjunctive tool for
caries prevention. This article aims to review existing literature on the effects of sugar substitutes on systemic and
oral health, and the possible mechanisms underlying these effects, especially those related to microorganisms.
Such information, integrating with data from future investigations, should be taken into consideration when advising
patients and the population on the use of sugar substitutes.
3
Page : 398-409Title : Caries Status and Risk Factors in 18 – 36 -Month-Old Children Attended Well Baby Clinic at Bangkok Metropolitan Administration General Hospital
Author(s) : Maetawee Angkatawanich, Siriruk Nakornchai
Keyword(s) : Caries,Debris score,Risk factors,Well baby clinic
Manuscript Type : Original Article (บทวิทยาการ)
Page : 398-409
This research aimed to study caries status and risk factors between socioeconomic status, oral health care
and dietary practices in 18-36-month-old children attended well baby clinic at Bangkok Metropolitan Administration
General Hospital. Cross-sectional analytical study conducted by recording tooth status, mean debris score and enamel
hypoplasia status of 320 children and interviewing their caregivers involving and socioeconomic status, oral health
care and dietary practices. Chi-square and Multiple logistic regression analysis were used to analyze the data. Fifty
four percent of children had dental caries. Mean dmft was 2.66 (± 0.21) teeth and mean decay was 2.7 (±3.8) per
child. Mean debris score 1.95 (± 0.8) and 39.7 % of children had enamel hypoplasia. The risk factors according to
Chi-square analysis were education levels and employment status of caregivers, age giving birth of mothers, media
consumption of caregivers and child medical welfare, oral cleaning, type of milk, feeding pattern, types of snacks
between meals, frequency of taking snacks and enamel hypoplasia. Multiple logistic regression showed that enamel
hypoplasia was the most significantly associated with dental caries, followed by mean debris score.
4
Page : 410-416Title : Relationship between Type of Patient Motivation and Severity of Orthodontic Treatment Need: A Study in Hat Yai, Songkhla, Thailand
Author(s) : Siritida Pongsupot, Supanee Sunthornlohanakul
Keyword(s) : Index of Orthodontic Treatment Need (IOTN),Motivation,Relationship
Manuscript Type : Original Article (บทวิทยาการ)
Page : 410-416
The purpose of this cross-sectional study was to evaluate the characteristics of patients seeking orthodontic
treatment and determine the relationship between the type of motivation and the level of orthodontic treatment
needed using the Dental Health Component of the Index of Orthodontic Treatment Need (DHC-IOTN). Samples of
this study included all consultation records of 2,008 patients from 2014-2017 who were aged over 12 years old
for determining the level orthodontic treatment need by DHC-IOTN. Descriptive analysis and chi-square test were
used in this study. Results showed most of the samples were female (74.3 %), aged 19-35 years old (47.9 %) with
internal motivation (52.0 %). The types of motivation of patients aged 7-12 years old and 19-35 years old were
mainly external and internal motivations, respectively. Samples were categorized as “Great need” (DHC grades 4-5)
about 50.5 %, while 33.6 % of them were in “No need” (DHC grades 1-2). There was no statistical relationship
between patient motivation and orthodontic treatment need level found in this study. So, it can be concluded that
female patients sought orthodontic treatment more than males. Late teenage-young adult patients made up the
main group of patients seeking orthodontic treatment driven mainly by internal motivation, while most childhood
patients were referred from general dentists and due to parental demand. About one third of patients were categorized
“No need” for orthodontic treatment and no statistical relationship was found between the type of patient motivations
and the severity of orthodontic treatment need.
5
Page : 417-430Title : Effectiveness of Brief Lifestyle Change Plus Dental Care (Brief-LCDC) Program in Improving Glycemic and Periodontal Status among Type 2 Diabetes Patients: A Clinical Controlled Trial
Author(s) : Saruta Saengtipbovorn
Keyword(s) : Oral health care,Lifestyle modification,Type 2 diabetes,Glycemic level,Periodontal status
Manuscript Type : Original Article (บทวิทยาการ)
Page : 417-430
The present study was a clinical controlled trial to assess the effectiveness of Brief Lifestyle Change plus
Dental Care program to decrease glycemic level and improve periodontal status in type 2 diabetes patients. The present
study was conducted in Diabetes clinic, Public Health Center 54 from February 2018 to February 2019. Diabetes
patients were divided to 96 patients for the intervention and 96 patients for the control groups. The intervention group
received group education for lifestyle modification, individual oral hygiene instruction, and lifestyle counseling by
motivational interviewing at baseline and the 6th month and received booster education every visit by viewing
educational video. Routine program was provided to the control group. At baseline, the 6th month and 1 year follow up,
glycemic level and periodontal status were assessed from the participants. Data were analyzed by descriptive statistic,
t-test, Chi-square test, Fisher’s exact test, Mann-Whitney U test, and Repeated measure ANOVA. The intervention
group had significantly lower glycemic level and periodontal status than the control group at the 6 month and 1 year
followed up. Brief-LCDC program which incorporated lifestyle modification and oral health care had efficacy to decrease
glycemic level and improve periodontal status in patients with type 2 diabetes. The prevention of diabetes complications
from early diagnosis is needed to prevent oral complications.
6
Page : 431-438Title : Clinical Outcomes of Dental Implants on Vascularized Fibular Bone Graft: Experience at Dental Hospital, Prince of Songkla University
Author(s) : Pichai Vittayakittipong, Thippapa Areewattana
Keyword(s) : Vascularized fibular bone graft,Clinical outcome,Dental implant
Manuscript Type : Original Article (บทวิทยาการ)
Page : 431-438
The aims of this study were to assess clinical outcomes and to analyze the related factors in the patients
who underwent osseointegrated dental implants on vascularized fibular bone graft at Dental Hospital, Prince of
Songkla University during A.D. 2009-2017. The demographic data, systemic diseases, medications, causes, length
and type of defect, and timing of reconstruction were collected. Conditions of bone and soft tissue before dental
implantation as well as data regarding dental implant installations and complications were collected. All patients
were recalled to assess subjective and objective clinical outcomes for calculating survival and success rate of dental
implants. The data were analyzed statistically using Chi-square (χ2) and Man-Whitney U test with the level of significance
at p<0.05. The result showed that ten patients were included in the study (3 males, 7 females) with mean age
37.0±13.6 years (range 21-60 years). Ameloblastoma was the most common cause of the defect (80 %). There were
9 mandibular and 1 maxillary defects. Mean defect length was 11.1±3.2 cm. Inadequate height of fibula for dental
implantation was found in 9 patients and corrected with an additional bone graft using iliac bone. Fifty dental implants
were placed on fibular bone graft with a mean of implant diameter was 4.2±0.7 mm. and of implant length was
13.3±1.6 mm. The survival and success rate of dental implants on vascularized fibular bone graft were 72 % and 65 %
respectively. The dental implant without prosthesis group had higher proportion of peri-implantitis than the dental
implant with prosthesis group significantly (p=0.01). The study concluded that clinical outcomes of dental implant
after oral and maxillofacial reconstruction with vascularized fibular bone graft are acceptable for oral rehabilitation.
Long-term maintenance for peri-implant tissue is necessary to increase the success and survival rate.
7
Page : 439-449Title : Evaluation of A Training Device for Practicing Indirect Vision for Dental Students, Thammasat University
Author(s) : Nattira Suksudaj, Kanokorn Yooyeun, Meanna Surapolchai, Natasit Punsorn
Keyword(s) : Mouth mirror,Indirect vision,Validity,Dental students
Manuscript Type : Original Article (บทวิทยาการ)
Page : 439-449
This study aimed to evaluate construct validity and face validity of a new training device for practicing
indirect vision in dental work. The study was undertaken at Faculty of Dentistry, Thammasat University. Forty-two
participants were divided into three groups (n=14 in each group) as novices (second-year students), competences
(sixth-year students) and experts (dental practitioners). All participants completed four drawing exercises, which
were attached on the training device, with indirect vision using mouth mirror. Construct validity was evaluated
by comparing time spent and errors in each exercise among the three groups. To assess face validity, expert and
competence groups completed a 5-point rating scale questionnaire concerning various aspects of training realism
and usefulness in learning indirect vision skill. The rating scale ranges from 5=strongly agree to 1 strongly disagree.
The results showed that experts performed significantly fewer errors than novices in most exercises (p<0.05).
However, there was no statistically significant difference in mean time spent among the three groups. Most of the
participants rated high scores on helpfulness of the training device for learning indirect vision, and its realism in
comparison with performing mirror-inverted movement in clinical situation. In conclusion, the face validity of the
training device could be established. The training device was able to differentiate the level of indirect vision skill in
dental practice, which demonstrated construct validity of this new device. Overall, the findings of the study support
that this device has a potential for training indirect vision skill in pre-clinical dental students.
8
Page : 450-455Title : The cross-cultural adaptation for Patient’s Denture Assessment Thai version (PDA-T)
Author(s) : Orapin Komin, Sahaprom Namano
Keyword(s) : Patient’s Denture Assessment (PDA),cross-cultural adaptation,Oral Health-related Quality of Life,complete denture
Manuscript Type : Original Article (บทวิทยาการ)
Page : 450-455
This study aimed to present the process of cross-cultural adaptation to develop to a Thai version of the
Patient’s Denture Assessment (PDA-T) from the Japanese original version. It is a self-assessment for the patients
who wear complete dentures to evaluate six aspects, which are Function, Esthetics and Speech, Lower Denture,
Expectation of Improvements with New Dentures, Upper Denture, and the Importance of Complete Dentures to
the Patient. Then, check for the content validity with the face validity. Using this assessment can be beneficial in
making a diagnosis, determining the prognosis, and comparing the efficacy of a complete denture (before and after
the treatment). Each question is measured using a horizontal 100-mm visual analog scale (VAS). However, an extra
question is added into the Thai version. The content validity and face validity were assessed in a sampling of 33
people (11 males and 22 females with an average age of 70.36 years old). The participants were instructed to read
each question and mark an outcome to represent their situations by a vertical line through the horizontal VAS in
each question. The PDA-T indicated good content validity after the initial test. Further research is recommended
for the process of the psychometric, reliability, validity and responsiveness properties of the PDA-T.
9
Page : 456-464Title : 4- and 7-module Elastomeric Chains Undergo Differential Force Decay in Artificial Saliva
Author(s) : Thanit Charoenrat, Korapin Mahatumarat
Keyword(s) : Force decay,force relaxation,force degradation,elastomeric chains,memory chains
Manuscript Type : Original Article (บทวิทยาการ)
Page : 456-464
Objective: To compare the remaining force between 4- and 7-module memory elastomeric chains (ECs)
Dyna-Link (D), Power Chain generation II (P), and Super Chain (S) (D4, P4, and S4 and D7, P7, and S7 groups) and
to compare the remaining force between the 4- and 7-module ECs in each brand (D4-D7, P4-P7 and S4-S7 groups)
during simulated canine retraction. Materials and methods: ECs were divided into six groups (D4, P4, S4, D7, P7, and
S7 groups) (n=10). The samples were stretched using a Universal Testing Machine to obtain an approximately 150
grams force and the stretch distance was maintained using pinned blocks which kept in artificial saliva at 37ºC. The
remaining force in each sample was measured after three and 24 hours, three days, and one, two, three and four
weeks. Statistical analysis was performed using the SPSS program. Results: Comparing the 4-module groups, the
D4 group demonstrated the significantly lowest remaining force at three days. The S4 group had the significantly
highest remaining force at one week. The significantly lowest remaining force was seen in the P4 group from 2–4
weeks. When 7-module groups were compared. The S7 group demonstrated the highest remaining force, while the
D7 group presented the lowest remaining force from 3 hours - 4 weeks. Comparing the 4- and 7-module groups,
the S7 and P7 groups had a significantly higher remaining force compared with the S4 and P4 groups, respectively.
Conclusion: When an initial force of 150 grams was applied, the S7 group demonstrated the highest remaining force
over four weeks. When using ECs for retracting teeth, 7-module chains are preferable compared with 4-module chains.
10
Page : 465-474Title : Sensitivity, Specificity and Profile of Direct Immunofluorescence in Oral Lichen Planus
Author(s) : Patrayu Taebunpakul, Aroonwan Lam-Ubol
Keyword(s) : Autoimmune diseases,Diagnosis,Direct immunofluorescence,Histopathology,Oral lichen planus
Manuscript Type : Original Article (บทวิทยาการ)
Page : 465-474
Oral lichen planus (OLP) is a chronic immune-mediated mucocutaneous disease. The clinical features of
OLP can sometimes resemble several autoimmune diseases. The histopathology and direct immunofluorescence
(DIF) are useful methods to confirm the diagnosis. Our aim was to evaluate the sensitivity and specificity of DIF in
OLP diagnosis. OLP DIF profiles were also investigated. Patients attending Oral Medicine Clinic, Faculty of Dentistry,
Srinakharinwirot University with the clinical diagnosis of OLP were recruited. The demographic data, histopathology
and DIF results, were collected from the patient records. Descriptive statistic was used to analyze the data. Fiftyseven
patients were included. The mean age±SD was 52.25+12.93 years. Male to female ratio was 1:6. The final
diagnosis based on clinical features, histopathology and DIF results was 46 cases of OLP and 11 of others. The
sensitivity and specificity of histopathology in OLP diagnosis were 84.78 % and 90.91 % in that order. While those of
DIF were 86.96 % and 100 % respectively. The shaggy fibrinogen deposition at the basement membrane zone (BMZ)
was found the most in 84.78 % of the OLP cases. The percentage of OLP diagnosis was increased when histologic
features and DIF profiles were included. To conclude, the sensitivity of histopathology is comparable to that of
DIF in OLP diagnosis. Both techniques demonstrate high specificity. Most common immune deposition in OLP is
fibrinogen. Therefore, clinical, histopathological and DIF features should be utilized for OLP diagnosis, especially in
cases that lack clinical characteristics.
11
Page : 475-482Title : The Effect of Scanning Sequence and Partial Edentulism on the Accuracy of Full Arch Digital Impression at Posterior Teeth
Author(s) : Chakree Ongthiemsak, Tewarit Saeyib
Keyword(s) : Digital impression,Intra-oral scanner,Accuracy,Scanning sequence,Partial edentulism
Manuscript Type : Original Article (บทวิทยาการ)
Page : 475-482
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the accuracy on posterior teeth of full arch digital impression in
different scanning sequences on fully dentate and partial edentulism by two intraoral scanners (TRIOS® and 3MTM
True Definition). Two dental models were prepared: fully dentate and partial edentulism of maxillary right second
premolar and maxillary right first molar. Full arch scans started from right to left were compared with the reverse
direction (n=10). Only digital data on maxillary right first premolar and maxillary right second molar from STL files
were superimposed within group to evaluate precision and superimposed with the reference scan (high accurate
scanner) to evaluate trueness using Geomagic Qualify 2013. Kruskal-Wallis test was implemented to compute precision
(α=0.05) and the results showed that precision of all groups were not different. Three-way ANOVA was used to analyze
trueness (α=0.05) and the results showed that TRIOS® had significantly lower mean deviation (12.86 ± 3.81μm)than
3MTM True Definition (15.03 ± 4.17 μm) (p=0.013). TRIOS® scanned on fully dentate model had significantly higher mean
deviation (14.71 ± 3.91 μm) than partial edentulous model (11.01 ± 2.71 μm) (p=0.003). No statistically significant
difference between scanning sequences was observed. In conclusion, intraoral scanner, scanning sequence and partial
edentulism did not affect the precision. TRIOS® had better trueness than 3MTM True Definition. Partial edentulous
model scanned with TRIOS® was found to have higher trueness than fully dentate model. No matter whether the full arch
scanning started from any quadrant, it did not affect the trueness on the posterior data when considered in ashort span.
12
Page : 483-491Title : The Association Between Body Mass Index and the Number of Healthy Teeth of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Author(s) : Piyamas Aemaimanan
Keyword(s) : Number of healthy teeth,Body Mass Index,Diabetes type 2
Manuscript Type : Original Article (บทวิทยาการ)
Page : 483-491
This study compared the number of healthy teeth in type 2 diabetes (T2D) patients who had varying body
mass index (BMI) and assessed the association and predictive factors for the number of healthy teeth of T2D patients.
A cross-sectional analysis is conducted on data of T2D patients who registered with 30 of the 2012 mobile medical
units, received general and dental examinations and were interviewed on general behaviors, with laboratory test
results less than three months older before the examination date. The data include medical evaluations in the 2012
diabetes examination surveys in 30 District Health Promotion Hospital in Selaphum-Thung Kao Luang District, Roi-Et
Province. The sample of 352 was divided into 2 groups: normal and obese groups, each group with 176 subjects.
The normal group had a normal BMI, while the obese group had extreme obesity. Mann-Whitney U test was used
to compare data between the two groups. Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient and multiple linear regression
were used to evaluate the correlation of variables. The study showed that the number of healthy teeth of normal
group was significantly higher than the obesity group (p<0.05). Most of the variables had a negative correlation with
the number of healthy teeth except for height. Among the variables, age and BMI are the strongest predictors of
the number of healthy teeth. T2D patients with obesity may be at risk of tooth loss more than patients who had
normal BMI, which affects the quality of life in the future.
1
Page : 247-259Title : Root Canal Irrigants: Considerations for Success in Pulp Treatment for Primary Teeth
Author(s) : Siriporn Songsiripradubboon, Nattanan Govitvattana
Keyword(s) : Pulp treatment,Irrigant,Primary teeth
Manuscript Type : Review Article (บทความปริทัศน์)
Page : 247-259
The aim of the pulp treatment in primary teeth is to preserve and maintain fully functional primary teeth in the dental arch until the time of natural exfoliation. It is well studied that microorganisms are considered to be
a major cause of pulpal and periapical pathosis. Therefore, the primary goal of pulp treatment is to eliminate or reduce microorganisms inside an infected root canal system. Root canal cleaning with irrigating solutions becomes one of the standard protocol as it can remove microorganisms, tissue debris, and smear layer efficiently. Various irrigating solutions have been suggested for pulp treatment in primary teeth. Different irrigants have distinct properties and, thus, present with different advantages, disadvantages and limitations. In clinical practice, these properties need to be considered, in particular, when using in pediatric patients. The objective of this article is, therefore, to review the various irrigating solutions commonly used in pulp treatment in primary teeth in many aspects. The mechanisms of actions, effectiveness, and their side effects are discussed. This information would be useful for clinicians to choose an irrigant during pulp treatment procedure.
2
Page : 260-270Title : Periodontal Tissues After Level and Align Lower Anterior Teeth in Nonextraction Orthodontic Treatment
Author(s) : Pornpat Theerasopon, Chairat Charoemratrote
Keyword(s) : bony dehiscence,Curve of Spee,crowding,mandibular incisor,gingival recession
Manuscript Type : Review Article (บทความปริทัศน์)
Page : 260-270
Non-extraction orthodontic treatment for crowding correction usually found labial movement of lower incisors. Alveolar bone which covers at labial surface of lower incisors found high incidence of bony dehiscence despite of patients who did not undergo an orthodontic treatment. This review article is aimed to propose the factors affecting labial movement of lower incisors, the results of gingival recession and alveolar bone loss after labial movement of lower incisors for the purpose in orthodontic treatment plan consideration which is not harmful to periodontal tissues.
3
Page : 271-280Title : The Study of Difference in Clinical Tooth Color Measurement among Visual Method Using White Light Box, Intraoral Scanner and Spectrophotometer
Author(s) : Chaivut Prunkngarmpun, Paweena Sangasaeng, Wilawan Weraarchakul
Keyword(s) : Intraoral scanner,spectrophotometer,tooth color measurement
Manuscript Type : Original Article (บทวิทยาการ)
Page : 271-280
The aims of study were to compare visual method using white light box, intraoral scanner and spectrophotometer in clinical tooth color measurement and to determine the reliability of tooth shade selection among visual method using white light box, intraoral scanner and spectrophotometer. Forty maxillary right central incisors and canines of 18 – 40 years old volunteers which no pathologic and restoration teeth were included in this study. Each tooth shade was measured six times, twice for each method with at least one day apart. Tooth color measurements were described in L* a* b*and tooth color difference (ΔE) according to CIELAB color system. In this system ‘L’ is a lightness coordinate, ‘a’ is a redness-greenness coordinate and ‘b’ is a yellowness-blueness coordinate. The Kruskal – Wallis statistic was used to verify the significant difference of average color difference (ΔE) at P<0.05. Results indicated significance difference in L* a* b* among all three methods. The average color difference (ΔE) of visual method were higher than the intraoral scanner method on both maxillary central incisor (8.05 versus 4.99) and canine (9.5 versus 4.95). Average reliability of visual method was 0.63 (range 0.56-0.69) in maxillary right central incisor and 0.63 (range 0.61-0.53) in canine while average reliability of intraoral scanner method was 0.70 (range 0.60-0.76) in maxillary right central incisor and 0.82 (range 0.63-0.91) in canine. Average reliability of tooth shade selection using spectrophotometer was highest at 0.87 (range 0.70-0.96) in maxillary right central incisor and 0.88 (range 0.76-0.95) in canine. In conclusion, average color difference (ΔE) from visual method is higher than intraoral scanner. Tooth color measurement using spectrophotometer is the most reliable method followed by intraoral scanner and visual method is the lowest.
4
Page : 281-290Title : Alveolar Bone Macroscopic Changes as a Response to Light Controlled-tipping Maxillary Dental Arch Expansion in Young Adults: A Cone-beam Computed Tomography Study
Author(s) : Udom Thongudomporn, Chanchai Pattanaviriyapisan, Chairat Chareomratrote
Keyword(s) : Cone-beam computed tomography,Slow maxillary expansion,Alveolar bone change,Light force
Manuscript Type : Original Article (บทวิทยาการ)
Page : 281-290
The objectives of this study were to examine the amount of expansion, the changes of molar inclination,
crown and root position of maxillary first molars, as well as changes of alveolar bone thickness, alveolar bone height
and buccal bone position by using cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) after light controlled-tipping expansion
in young adult subjects. Factors related to changes in alveolar bone thickness (ABT) were also investigated. Maxillary
dental expansion was performed in twenty-four patients (age 15.3-26.5-year-old) with orthodontic fixed appliances
and a straight rectangular titanium molybdenum alloy (TMA®) wire which produced 126 ± 27 g of expansion force.
Dento-alveolar changes were evaluated using CBCT images acquired before (T0) and 3 months after expansion (T1).
Mann-Whitney U-tests, Wilcoxon matched pairs signed rank tests, Kruskal-Wallis test with the Dunn-Bonferroni tests
were used to compare the changes. Spearman’s rank correlation analysis was performed to identify factors associated
with the changes of ABT. The significance level was set at .05. Significant buccal controlled-tipping of the first molars
occurred leading to a significant increase of intermolar width (IMW) (P<0.01). ABT at bucco-crestal site of mesio-buccal
root (ABT-MB-L1) significantly decreased (P<0.05), while ABT at palatal sites (ABT-Pa) significantly increased (P<0.05).
Buccal bone position (BucBonePos) significantly displaced buccally (P<0.05). ΔIMW and the rate of expansion significantly
positively related to ΔABT-MB-L1 (P<0.05). Initial ABT was significantly negatively correlated with ΔABT-MB-L1 and
ΔABT-Pa (P<0.05). The study concluded that some degrees of ABT-MB-L1 reduction and ABT-Pa gain were observed
when applying force lower than 130 g for controlled-tipping maxillary dental arch expansion. These changes were
related to ΔIMW, rate of expansion, and initial ABT. Buccal displacement of outer surface of bucco-crestal bone
was observed.
5
Page : 291-302Title : The Effects of Adlay Extract on Primary Human Osteoblast Cells: Cytotoxicity and In vitro Calcification
Author(s) : Thidarat Angwarawong, Nareekarn Chantakanakakorn, Niracha Chareonkitjatorn, Onauma Angwaravong, Warinthon Triwatana
Keyword(s) : In vitro calcification,cytotoxicity,primary human osteoblasts,adlay extract
Manuscript Type : Original Article (บทวิทยาการ)
Page : 291-302
Osteoporosis is one of the major public health problems of the world. The disease causes the loss of bone mass and degeneration of bone microarchitecture resulting in decreased bone strength and osseointegration process is also affected in implant patient. In the past decade, a large number of research on various natural products has been conducted to find a way to prevent osteoporosis and promote osteogenesis. It has been revealed that adlay extract can increase cell proliferation and upregulates alkaline phosphatase activity, calcium level and bone density in mouse model. However, there is a lack of the study on the effect of adlay extract on primary human osteoblasts. This research thus aimed to examine the cytotoxicity and in vitro calcification of adlay extract on human osteoblasts. Cytotoxicity was evaluated using MTT assay, testing adlay extract at concentration of 3, 15, 30, 150, 300, and 600 μg/ml prepared in DMEM with 2 % and 15 % fetal bovine serum (FBS) at 24, 48, and 72 hours. Alizarin Red-S staining was used to analyze in vitro calcification of osteoblasts cultured in DMEM containing 15 % FBS and different concentrations of adlay extract and at 14 and 21 days. Results from this study showed that 3-600 μg/ml adlay extract had no toxic effect on primary human osteoblasts, and that 150, 300 and 600 μg/ml adlay extract promoted cell proliferation when compared to control group at 72 hours in both 2 % and 15 % FBS in DMEM. Furthermore, 3-600 μg/ml adlay extract increased in vitro calcification. This study served as initial information for its future use for surface modification of dental implant in patient with osteoporotic bone.
6
Page : 303-311Title : Characteristics of Gingival Biotype of Maxillary Incisors in Thai Young Adults
Author(s) : Kajorn Kungsadalpipob, Pimchanok Sutthiboonyapan, Kraisorn Arsathong, Jutarat Phuensuriya, Jatupon Fuengfu, Hom-Lay Wang
Keyword(s) : Gingival phenotype,Gingival biotype,Papilla height,Tooth shape,Maxillary incisors
Manuscript Type : Original Article (บทวิทยาการ)
Page : 303-311
The aim of this study was to determine gingival phenotype prevalence and characteristics in maxillary incisors in young adults. The maxillary incisors of 100 periodontally healthy subjects (mean age 22.20±0.84 years) were
examined by 2 calibrated examiners. The gingival phenotype was identified using transparency probing and visual inspection. Clinical parameters; probing depth, gingival recession, clinical attachment level, gingival width, papilla height, and tooth shape were determined. Descriptive analysis was performed and the clinical parameters between gingival phenotypes were compared using the t-test and ANOVA. The result demonstrated that maxillary incisor teeth displayed a thin phenotype (66 %) when assessed using probe translucency. The gingival phenotype was associated with tooth shape (p<0.01). Thin gingival phenotype had a significantly narrower gingival width, but higher papilla height compared with the thick phenotype (p<0.001). A scalloped gingival contour was noted when the papilla height was more than or equal to 4 mm. A thick-flat, thick-scalloped, and thin-scalloped contour was associated with square, ovoid, and triangular tooth shape, respectively. In conclusion, most subjects demonstrated a thin gingival phenotype. The thin phenotype was associated with higher papilla height and triangular tooth shape, while the thick phenotype was associated with broader keratinized tissue width and ovoid/square tooth shape.
7
Page : 312-323Title : Association of Skeletal Bone Mineral Density and Periodontitis in Postmenopausal Women of the Electricity Generating Authority of Thailand (EGAT)
Author(s) : Rapatchata Suthasinekul, Sanutm Mongkornkarn, Chanika Sritara, Attawood Lertpimonchai, Suphot Tamsailom, Artit Udomsak
Keyword(s) : Bone density,Osteoporosis,Periodontal-systemic disease interactions,Periodontitis,Postmenopausal
Manuscript Type : Original Article (บทวิทยาการ)
Page : 312-323
This study aimed to investigate the association between skeletal bone mineral density (BMD) and periodontitis in postmenopausal women of the Electricity Generating Authority of Thailand (EGAT) workers. This cross-sectional study comprised of 395 postmenopausal women, aged 35-82 years old. BMD was assessed at three skeletal sites by using dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry. BMD values at each site were converted into T-scores. The t-score at the worst site was used to categorize each participant into osteoporosis, osteopenia, or normal BMD groups. The periodontal assessments included probing depth (PD), clinical attachment level (CAL), plaque score, and number of remaining teeth. The participants were classified into the no/mild periodontitis or moderate/severe periodontitis groups. The mean BMD between the periodontitis groups and the mean periodontal variables between BMD categories were compared. The degree of association between the BMD groups and periodontitis, adjusted for known confounders, was analyzed using binary logistic regression. Comparing the two periodontitis groups, there was no significant difference in the mean BMD at any skeletal sites or at the worst site. Among the BMD groups, there was no significant difference in mean number of remaining teeth, mean PD, and mean plaque score, while the mean CAL difference of 0.3 mm was demonstrated between the osteopenia and osteoporosis groups. (P<0.001). After adjusting for confounders, there was no significant association between osteoporosis and periodontitis in postmenopausal participants, whereas increasing age and plaque score > 40 % were the factors significantly associated with moderate/severe periodontitis (P<0.05). There was no significant association between osteoporosis and periodontitis in postmenopausal women of the EGAT population. However, studies in various populations should confirm this finding.
8
Page : 324-333Title : Effects of Blood Contamination on Apatite Formation, pH and Ion Release of Three Calcium Silicate-based Materials
Author(s) : Chootima Ratisoontorn, Nareerat Thanavibul, Anchana Panichuttra
Keyword(s) : Apatite formation,Blood contamination,Calcium silicate-based materials,Ion release
Manuscript Type : Original Article (บทวิทยาการ)
Page : 324-333
The aim of this study was to assess the effects of blood contamination on the apatite formation, pH and ion release of three calcium silicate-based materials. ProRoot MTA (WMTA), Biodentine and TotalFill BC RRM putty
(TRRM) were exposed to blood (blood-contaminated condition) or normal saline (non-blood-contaminated condition) for 24 hours. Samples were divided into 6 groups: WMTA without blood, WMTA with blood, Biodentine without blood, Biodentine with blood, TRRM without blood and TRRM with blood. Three samples of each group were analysed for apatite formation using X-ray diffractometer (XRD) and an energy-dispersive X-ray spectoscope (EDX) integrated into a scanning electron microscope (SEM) after immersion in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) for 1, 7, 14 and 28 days. Five samples of each group were used to measure pH, calcium and silicon ion release using a pH meter and inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectrometer (ICP-OES) after immersion in deionized water for 1, 7, 14 and 28 days. Apatite formation was found in the blood-contaminated groups later than the non-blood-contaminated groups. In both conditions, WMTA demonstrated apatite formation earlier than other materials. The pH and calcium ion release of the materials were not significantly affected by blood contamination (P>0.05). Silicon ion release was reduced in all blood-contaminated groups (P<0.05). Blood contamination delays apatite formation and decreases silicon ion release of calcium silicate-based materials.
9
Page : 334-342Title : Vertical Skeletal Pattern influences Alveolar bone Thickness in the Anterior Mandible of Thais
Author(s) : Phuntin Uengkajornkul, Korapin Mahatumarat, Soontra Panmekiate
Keyword(s) : Alveolar bone thickness,Cone-beam computed tomography,Mandibular incisors,Vertical skeletal pattern
Manuscript Type : Original Article (บทวิทยาการ)
Page : 334-342
This study evaluated the alveolar bone thickness (ABT) of the mandibular incisors in Thais with different vertical skeletal patterns. One hundred and thirty-five patients (average age 24.2 years) were divided into three
groups according to their vertical skeletal pattern (i.e. skeletal deepbite, skeletal normal bite, and skeletal openbite). The labial and lingual ABTs of the mandibular incisors at 3 mm (cervical level) and 6 mm (mid-root level) apical to the cemento-enamel junction (CEJ) and at the root apices (apical level) were measured from cone-beam computed tomography images. One-way ANOVA was used to determine the differences in ABT between the groups at a 0.05 significance level. There were the differences in ABT between the three groups (p<0.001), with the greatest difference seen between the skeletal deepbite and openbite patients. The skeletal deepbite patients had the significantly thickest labial and lingual alveolar bones of the mandibular incisors followed by the skeletal normal bite and skeletal openbite patients, which were also significantly different from each other, at the lingual mid-root and total apical ABT. In conclusion, considering the alveolar bone as the boundary for tooth movement, greater movement of the mandibular incisors in an antero-posterior direction can be performed in skeletal deepbite patients, while skeletal openbite can undergo the least movement, mainly at the lingual mid-root and root apex levels.
10
Page : 343-352Title : How Thick Peri-implant Tissue Affected Esthetic Satisfaction on Single Implant Restoration in Treated Periodontal Patients
Author(s) : Sirikarn P. Arunyanak, Tharntip Suwanwichit, Navawan Sophon, Teerawut Tangsathian, Kakanang Supanimitkul, Kajorn Kungsadalpipob
Keyword(s) : dental implant,esthetic,patient satisfaction,periodontitis,visual analogue scale
Manuscript Type : Original Article (บทวิทยาการ)
Page : 343-352
To identify the factors affecting the esthetic outcome of implant-supported single crowns in periodontal patients, thirty-four periodontitis patients with implants were consecutively examined for esthetic outcomes. A
questionnaire was used to measure the satisfaction of patients with peri-implant soft tissues, implant crown, smile, and total implant treatment using a visual analogue scale (VAS). Ten clinicians applied the Pink and White Esthetic Score (PES/WES) to each patient. The association between the clinical factors and the degree of patient satisfaction was analyzed using the Pearson chi-square test. The mean overall patient’s satisfaction was 80.2 % and the mean PES/WES was 12.67. Peri-implant tissue biotype was significantly associated with the degree of patient satisfaction on papilla height, contour, color, and labial mucosa surface. A thick peri-implant tissue was the only significant factor in determining the degree of patients’ satisfaction in periodontal patients. However, all patients reported acceptable esthetic outcomes.
11
Page : 353-360Title : Shear Bond Strengths of Zirconia/Resin Cement Using Different Adhesives
Author(s) : Awiruth Klaisiri, Nantawan Krajangta, Tool Sriamporn, Niyom Thamrongananskul
Keyword(s) : Shear bond strength,Zirconia,Resin cement,Adhesive,MDP
Manuscript Type : Original Article (บทวิทยาการ)
Page : 353-360
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effects of two different adhesives containing phosphate
monomer [Single Bond Universal+dual activator (SU), Excite F DSC (EX)] and one primer containing MDP [Alloy
primer (AP)] application on zirconia/resin cement bond strength. Sixty zirconia disks (6 mm diameter, 4 mm thick)
were prepared and embedded in dental gypsum. Specimens were polished with 600 grit silicon carbide paper. The
samples were randomly divided into six groups (N=10 in each group) according to different treatments applied on
zirconia surfaces: Group1 (AP), Group2 (SU), Group3 (AP+SU), Group4 (EX), Group5 (AP+EX) and Group6 (no tx). A
silicone template (3 mm diameter, 2 mm thick) was placed on top of treated zirconia surface. The resin cement
was filled into the mold and then light-cured for 40 seconds. All bonded specimens were kept in distilled water at
37oC for 24 hours and they were subjected to shear bond strength measurement using a universal testing machine
at a crosshead speed of 0.5 mm/min. The data were statistically analyzed using one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s test
(α=0.05). The shear bond strengths of Group1 to Group 6 were AP;14.12±2.56, SU;19.25±2.00, AP+SU;23.53±2.15,
EX;18.93±1.93, AP+EX;22.91±2.14, and no tx;8.05±1.64 MPa, respectively. The bond strengths of Group3 and Group5
were significantly higher than those of Group1, Group2, Group4, and Group6 (p<0.05). However, Group6 showed the
lowest bond strength (p<0.05). In conclusion, the primer containing MDP application followed by adhesive application
increased shear bond strength between zirconia and resin cement. The universal adhesive/adhesive containing
phosphate monomer may be alternative to the primer containing MDP for zirconia surface treatment.
12
Page : 361-368Title : Efficacy of Articaine Infiltration for Pulp Treatment in Mandibular Primary Molars: A Randomized Split-mouth Clinical Trial
Author(s) : Siriruk Nakornchai, Anchana Areethamsirkul, Benjamas Apipan
Keyword(s) : Articaine,Infiltration anesthesia,Primary molar,Pulp treatment
Manuscript Type : Original Article (บทวิทยาการ)
Page : 361-368
This clinical trial aimed to compare pain scores and adverse events between buccal infiltration with 4 % articaine with epinephrine 1:200,000 and nerve block with 2 % lidocaine with epinephrine 1:100,000 in pulp treatment in mandibular primary molars. Twenty-six children received pulp treatments on both sides of the mandible with inferior alveolar nerve block with lidocaine and buccal infiltration with articaine in random sequences. Pain scores were assessed during injection and pulp removal by video observation and through participant’s self-reporting after the procedure. Additional local anesthesia and adverse events were monitored. The Wilcoxon Signed-Rank test and the McNemar test were used for statistical analysis. Pain scores during injection in lidocaine nerve block (2.4±1.2) and articaine infiltration (1.7±0.9) were significantly different (p=0.002). There was no statistical difference in pain scores during pulp removal, overall pain from self-reporting and additional local anesthesia. One case in each method reported lip biting after treatment. No other adverse events were reported in this study. In conclusion, mandibular infiltration with articaine was not different from inferior alveolar nerve block with lidocaine in pain control and adverse events when performing pulp treatment in mandibular primary molars; however, it provided less pain during injection.
1
Page : 110-125Title : Free Sugars: The Cause of Dental Caries
Author(s) : Sudaduang Krisdapong, Panida Thanyasrisung
Keyword(s) : sugars,prevention and control,dental caries,non-communicable chronic diseases,health promotion
Manuscript Type : Review Article (บทความปริทัศน์)
Page : 110-125
Dental caries is the most important oral disease, the main cause of oral impacts on quality of life. Treating new and recurrent caries throughout life requires huge amount of dental resources. Caries is preventable. Free
sugars or non-milk extrinsic sugars (NMES) are the main cause of caries. Free sugars are all mono/disaccharides in processed grain, vegetables and fruits, including honey, natural syrup and fruit juice; with an exception of sugars naturally present in milk. Free sugars are mostly presented as added or table sugars. Toothbrushing is inadequate for caries prevention because caries generally occurs in small grooves and concave areas on proximal surfaces which are not reachable by toothbrush and dental floss. Fluoride can help reducing caries, however, with a limitation. Reducing sugars consumption is therefore, the key to caries prevention. Studies on sugars and caries have been conducted for nearly 80 years which provides the established evidence on sugars as the cause of caries. Sugars lead to the change of oral environment which increase the proportion of cariogenic microorganism in dental plaque. Sugars are also the cause of non-communicable chronic diseases (NCD) such as obesity, diabetes and hypertension. World Health Organization published guideline on sugar consumption for preventing caries and NCDs. The relationship between sugars and caries is linear. Caries increases by the increase of sugars consumption, without safe zone. Moreover, caries increases continuously by age. Thus, to reduce caries for the whole lifespan, sugar consumption should be as low as possible, particularly in children. A maximum of sugar consumed is 25 gram per day. Controlling the amount of sugars consumed is necessary for general health, however, limiting the frequency of consumption is more practical and directly relevant to caries control. Sugar-added snacks and drinks should be consumed during mealtimes. Consumption between meals should be limited to once a day. Sweetness or sugar concentration should also be reduced, particularly in drinks which are the main source of sugar overly consumed. Drinks should be no sugar-added or not more than 6 % sugar content. Water and plain milk are the best choices.
2
Page : 126-133Title : Application of Platelet-Rich Plasma in Orthodontics
Author(s) : Bancha Samruajbenjakun, Theerasak Nakornnoi
Keyword(s) : Tooth movement,Growth factors,Cytokines,Orthodontics,Platelet-rich plasma (PRP)
Manuscript Type : Review Article (บทความปริทัศน์)
Page : 126-133
In orthodontics, the methods for accelerated tooth movement are increasingly interested in the research for reducing the effects of the long treatment time. Platelet-rich plasma is a rich source of growth factors, which
are critical in the tissue remodeling process of tooth movement. Moreover, it contains the inflammatory cytokines. It is known that orthodontic tooth movement can be described as an inflammatory process. Therefore, the application of platelet rich plasma exhibits a good potential to enhance the rate of tooth movement. Several studies have been reported the efficient use of platelet rich plasma to increase the rate of tooth movement. The objectives of this review article are to demonstrate the use of platelet rich plasma in orthodontics and its effect on orthodontic tooth movement.
3
Page : 134-142Title : Management of Class III malocclusion with Atypical Extraction
Author(s) : Thanit Charoenrat
Keyword(s) : Class III malocclusion,camouflage treatment,extraction
Manuscript Type : Case Report
Page : 134-142
A 28-year-old female with a skeletal Class III malocclusion, missing her upper first premolars, retroclined upper, lower incisors and premature contact at 21 and 31 that caused anterior sliding when she bit and her chin
shifted to the left was treated by orthodontic alone. Her lower second premolars (35, 45) and lower third molars (38, 48) were extracted during orthodontic treatment. Correction of the Class III malocclusion and upper space
closure were achieved by Class III elastics. Prevention of retroclination of lower incisors during space closure was performed by adding gable bend to arch wire. The active treatment period was 30 months. The one-year retention showed that the treatment results were quite stable.
4
Page : 143-150Title : The Management of Surgical Defect in A Patient with Stage I Low-GradeMucoepidermoid Carcinoma Using An Obturator Prosthesis: A Case Report
Author(s) : Panarat Kodkeaw, Chaiwat Songsermpanyakul
Keyword(s) : Surgery,Obturator,Early stage oral cancer,Oro-nasal communication
Manuscript Type : Case Report
Page : 143-150
This report presents a 64 year-old female patient with stage I low-grade mucoepidermoid carcinoma at the junction of the hard and soft palate on the left side. A wide excision was used to completely remove the cancer
with a negative margin control of at least five millimeters. The post-operative obturator was used to restore the palatal defect and the oral function. Tissue conditioner was used to line the obturator in the area close to the defect. This procedure helps to improve fit, control the nasal leakage, promote the wound healing, and reduce pain. During healing process, the obturator was adjusted and the tissue conditioner was changed periodically. Finally, the oro-nasal communication was spontaneously closed in three months after surgery. The oral function was returning to normal again.
5
Page : 151-161Title : Fracture Resistance of Endodontically Treated Premolars with Deep CervicalLesions Restored with and without Posts in Different Restorations
Author(s) : Phrohphrim Suebsawadphatthana, Chalermpol Leevailoj
Keyword(s) : Fracture load,onlay,CAD/CAM,fiber post
Manuscript Type : Original Article (บทวิทยาการ)
Page : 151-161
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effects of fiber posts and different restorations on the fracture resistance of endodontically treated maxillary premolars with cervical cavities. In forty extracted human first maxillary premolars, cervical cavities were prepared simulating cervical lesions and randomly divided into four groups (n=10): COM-NP, endodontically treated teeth (ETT) restored with resin composite without fiber posts; ON-NP, ETT restored with CAD/CAM ceramic onlays without fiber posts; COM-P, ETT restored with resin composite and fiber posts; and CR-P, ETT restored with CAD/CAM ceramic crowns and fiber posts. After the fiber posts and restorations had been cemented with resin cement, all specimens were loaded onto the long axis in a universal testing machine until fracture at a speed of 0.5 mm/min. Fracture load (N) and fracture modes were evaluated in all specimens. The mode of failure was determined by visual inspection. Data were analyzed with Welch’s ANOVA and Games-Howell tests (p<0.05). Fracture load for all groups were (N): COM-NP (933.48±242.53); ON-NP (1871.45±313.59); COM-P (1510.17±251.87); and CR-P (2189.97±600.38). COM-NP had the lowest fracture resistance, significantly different from those of the other groups (p≤0.05). Statistically significant differences were observed among groups (p≤0.05), except in the ON-NP to CR-P groups (p=0.471). All groups showed the non-restorable fracture mode. Cuspal-coverage restorations significantly enhanced the fracture resistance of endodontically treated maxillary premolars with cervical cavities. Placement of fiber posts improved the fracture resistance of endodontically treated teeth but did not make the failure restorable.
6
Page : 162-174Title : Effect of Immediate Dentin Sealing and Thermocycling on Microtensile BondStrength when Using A Three-step Etch and Rinse Adhesive
Author(s) : Saranpong Pantung, Sirivimol Srisawasdi
Keyword(s) : Immediate dentin sealing,Simulated dentinal fluid flow,Thermocyclingl,Microtensile bond strength,Three-step etch and rinse adhesive
Manuscript Type : Original Article (บทวิทยาการ)
Page : 162-174
The aim of this study was to compare the effect of immediate dentin sealing (IDS) on microtensile bond strength (μTBS) of resin composite restoration using a three-step etch and rinse adhesive under various thermocycling periods. Sixty-four extracted human third molars were divided into 6 groups (groups 1-3 = controls and groups 4-6 = experimentals) with 10 teeth in each group. The remaining 4 teeth were divided into groups 1 and 4 for scanning electron microscope (SEM) evaluation. Flat dentin surfaces were prepared, and a 3-step etch and rinse adhesive was applied as an IDS step after tooth preparation within experimental groups. All specimens were then contaminated with impressions and provisional restorations. After being stored for 1 week, all samples were restored using a composite resin under simulated fluid flow. Thermocycling was performed in all groups, and μTBS was measured at 0, 5,000 and 10,000 cycles, respectively. The specimens were then sectioned to obtain a bonded hourglass of 1.0 ± 0.01 mm2 in area. Microtensile bond strength was tested at a crosshead speed of 1.0 mm/min, and data analyzed using a Two-way ANOVA, One-way ANOVA and a Tukey’s post hoc test (α = 0.05). Specimens were also evaluated for modes of fracture using a stereomicroscope at 40X, and data analyzed using a Chi-square test (α = 0.05). Specimen surfaces and hybrid layers from groups 1 and 4 were also examined before and after restoration using a SEM analysis. Two-way ANOVA showed significant difference among IDS and thermocycling cycles. An interaction was not observed. One-way ANOVA showed the mean μTBS of control group was statistically different from those of experimental group of the same thermocycling cycles. In the same IDS condition, statistically significant decrease in bond strength was found in 10,000 cycle-thermocycling group, when compared to immediate bond strength (after 24 hours) group. Microscopic evaluation indicated that most failures in all groups were adhesive and mixed failures. SEM analyses of the dentin surface and hybrid layers showed dentinal tubules obstruction in the experimental groups.
7
Page : 175-184Title : Effect of Ultrasonic Treatment on The Leachable Monomer Content fromA Self Cured Acrylic Hard Denture Reline Material
Author(s) : Chairat Wiwatwarapan, Pawilai Arriwiratchakun
Keyword(s) : High pressure liquid chromatography,Leached monomer,Acrylic resin,Hard reline,Ultrasonic
Manuscript Type : Original Article (บทวิทยาการ)
Page : 175-184
The aim of this study was to compare the amount of leachable monomer of a hard reline acrylic resin, after residual monomer reduction treatments, in water immersion at various times. Twenty-four specimens of an auto-polymerized acrylic hard denture reline material (Unifast Trad Pink) were prepared and divided into four groups (n= 6): Group 1 control, untreated; Group 2 water immersion at 50oC for 1 hour; Group 3 and 4 water and 30 % ethanol solution immersion at 50oC in ultrasonic bath for 5 minutes, respectively. Specimens were immersed in water 37oC. Water samples were taken from each immersion solution at the periods of 1, 3, and 24h and also at 3,7 days. The water samples containing leachable monomer were analyzed using HPLC following ISO 20795-1(2013). The data were analyzed by Two-way ANOVA, One-way and Dunnett’s T3 comparison test. All tests were performed at a confidence level of 95 %. The result showed that the amount of leached methyl methacrylate (MMA) in Group 2, 3 and 4 was significantly lower than that of Group 1 (p<0.05) but Group 1 and 2 was not significantly different in day 7 (p>0.05) and the amount of leached MMA in Group 1 and 2 was significantly higher than that of Group 4 (p<0.05) but there was not significantly different from that of Group 3 (p>0.05). In conclusion, water or 30 % ethanol solution immersion in ultrasonic post polymerization treatment at 50oC for 5 minutes of a hard reline acrylic resin significantly reduced the amount of leached MMA, which was better or similar than water immersion at 50oC for 1 hour and this method is more effective in clinical situation than presently recommended methods because of only 5 minutes immersion time.
8
Page : 185-197Title : Success Rate of Altered Resin Modified Glass-ionomer Cement Restorationson Teeth with Partial Caries Removal at 6 Months
Author(s) : Oitip Chankanka, Krongkan Thongrakkhao, Supitcha Talungchit, Pichanun Srisommai
Keyword(s) : Partial caries removal,Conventional glass-ionomer cement,Resin modified glass-ionomer cement,Primary molar,Caries
Manuscript Type : Original Article (บทวิทยาการ)
Page : 185-197
Restorative material that has good and appropriate properties may increase the success rate of partial caries removal restorations. The objective of this study was to assess and compare success rates of encapsulated
conventional glass-ionomer cement (GIC: Fuji IX GP® Extra Capsule) and Bulk fill altered resin modified glass-ionomer cement (RMGIC: ActivaTM BioACTIVE-RESTORATIVETM) on partial caries removal to DEJ in primary molars at the 6-month follow-up. Two hundred and sixteen healthy children aged 5-9 years old with occlusal caries (ICDAS scored 5) on a primary molar were enrolled in the randomized controlled trial. Children were randomly allocated into one of 2 groups: the control group (GIC) and the experiment group (RMGIC). For all selected teeth, partial soft caries removal at the dentin-enamel junction (0.5 millimeter from DEJ) was performed by a spoon excavator. Cavities were restored with materials according to the assigned studies groups. Clinical evaluation for modified ART codes, secondary caries, signs and symptoms, and radiographic examinations were conducted at the 6-month follow-up. The chi-square test for per-protocol and intention-to-treat analyses was performed. The success rates of restorations in the control and experiment groups when using the acceptable cutoff level of the modified ART codes (acceptable: code 0/1) with clinical and radiographic findings were 95.5 % and 87.6 %, respectively. There was no statistically significant difference in the success rates of restorations between the two groups (p>0.05). However, analysis using the “good level” of the modified ART codes cutoff (good: code 0) found that the control group had statistically significantly higher success rate than the experiment group (92.0 %vs.77.3 %) (p<0.01). The main reason for failure after 6 months was marginal defects. Thus, comparison using the “good level” cutoff showed that the encapsulated conventional GIC group had a higher success rate compared with bulk fill altered RMGIC in partial caries removal cavities.
9
Page : 198-208Title : Complications of Wisdom Tooth Removal by Non-Oral and MaxillofacialSurgeons: Rate and Related Factors
Author(s) : Khemakorn Wongkalasin
Keyword(s) : Complication,Removal,Wisdom tooth,non-oral and maxillofacial surgeon
Manuscript Type : Original Article (บทวิทยาการ)
Page : 198-208
Wisdom tooth removal has a wide range of potential complications. Most are insignificant, yet critical ones may result in irreversible consequences. In addition, the rate of complications varies widely and seems to be influenced by a variety of factors. However, there is limited knowledge about the complications, especially in contexts where oral and maxillofacial surgeons are unavailable. This retrospective cohort study aimed to determine the rate of complications in wisdom tooth removals by non-oral and maxillofacial surgeons and relating factors. Using a structured record form, this study collected data from dental records of patients who had their wisdom teeth removed between 2012 and 2017. Of the 898 teeth removed by nine non-oral and maxillofacial surgeons, 631 teeth (70.3 %) met the eligibility criteria. Ten types of signs and symptoms recorded in the operation, emergency and follow-up visits indicated the presence of complications. Multiple Logistic Regression and the Generalized Estimating Equation were used to analyze five potentially related factors. The findings showed that three-fourths of wisdom teeth were removed from female patients. The average age was 26.7±9.36 years old. The rate of complications was 12.0 % (95%CI 9.6-14.8). The first three complications were severe pain (4.9 %), alveolar osteitis (2.5 %) and incomplete root removal (1.5 %). The increasing of age by five years would lead to 27 % of developing complications (ORadj=1.27 95%CI 1.14–1.42 p < 0.001).
10
Page : 209-216Title : Relationship between Oral Status and Oral Health-Related Quality of Life of Early Privates in the Southern of Thailand
Author(s) : Samerchit Pithpornchaiyakul, Nutcharee Panicharoenrat, Sukanya Tianviwat
Keyword(s) : Oral health-related quality of life,Early private,Oral status
Manuscript Type : Original Article (บทวิทยาการ)
Page : 209-216
The purposes of this study were to survey oral status, oral health-related quality of life and to determine relationship between oral status and oral health-related quality of life of early privates in the southern of Thailand.
Study design was a cross-sectional analytical study. Samples were recruited by multistage random sampling from the second period in 2016 with 2 years of conscription. Data were collected by oral examination and questionnaire interviewing. The oral health-related quality of life questionnaire was tested on content validity and reliability. The results showed that 246 early privates had mean age 21.9±1.1 years old. The prevalence of decay, retained root, DMFT and impacted tooth were 81.3 %, 40.7 %, 85 % and 32.5 % respectively. Their mean decay, retained root, DMFT and impacted tooth were 4.2, 0.9, 5.1 and 0.5 teeth/person respectively. The mean of total OHIP-14 score was 8.25±8.73. Physical pain and psychological discomfort were the most affected dimension. Oral status that associated with oral health-related quality of life were retained root and impacted tooth. In conclusion, early privates with 2 years of conscription had many oral status problems, which associated with oral health-related quality of life. Early privates who had retained root or impacted tooth had worsen oral health-related quality of life.
11
Page : 217-236Title : Legal Effect of Social Media use of Dental Personnel
Author(s) : Adinant Prompanjai
Keyword(s) : Social media,Dental service,Personal medical information,National health commission,Dentist
Manuscript Type : Original Article (บทวิทยาการ)
Page : 217-236
The technologies have changed the way we communicate with others through the internet. The news and advertisement dissemination of both dentists and dental clinics is on the risk of violating the law. To present the
concern of government sector in the right of patients have affected the dental services. Structuralism was applied to analyze laws as a structure to set power relations between state and society. This concept helped to examine the new health care laws how they affected the dental services. According to the research, the patient profiles have been shared online, and with the serious competition between dental business, the owners promote their clinics on line. Thai government sector concerned about the right of patients should be protected as shown the declaration of National health commission: The practice of social media for health care staff. Not only it be concerned about disclosing of information privacy and personal medical information of patients but also had the other related laws as Child Protection Act, B.E. 2546 (2003), Thailand’s Computer-related Crime Act, B.E. 2560 (2017) and improved Sanatorium Act, B.E. 2559 (2016) to add penalty with imprisonment for prohibited advertising. The dentists and dental clinics should try to understand about position, duty and limitation of online communication to avoid infringement of the patients and protect the risk of offence the laws.
12
Page : 237-246Title : A Caries Risk Assessment Tool for Thai Children 3 Years Old or Younger
Author(s) : Oitip Chankanka, Pensiri Somsri, Sasima Khamleang, Sarinpan Klurvudthikul, Supreeya Sombut, Supatcha Lamlertwathee, Duangthida Paiboonwarachart
Keyword(s) : Dental caries,Caries risk assessment,Infant,Toddler
Manuscript Type : Original Article (บทวิทยาการ)
Page : 237-246
There is a need for caries risk assessment tools for very young children that have acceptable predictive power. The objectives of the present study were to construct and assess predictive abilities of a caries increment risk
assessment for very young children. Data collection was conducted from 133 pairs of children younger than 3 years old and their caregivers in child care centers. Caregivers were interviewed for caries related factors. Two dental examinations were conducted at baseline and about 6 months thereafter. The transition of caries between the two exams was classified into having caries increment or not. The data-splitting concept was used by dividing the data into 75:25 ratios. The larger part (75 %) was used to construct the assessment tool. Question selection for the tool was based on associations between caries associated factors and having caries increment using the chi-square test. Significant associated factors and factors tending to be associated with caries increment were selected for core and additional factors. Scores for core and additional factors were set. The total risk score for each child was calculated and then used to find a cutoff that gave the highest sum of sensitivity and specificity associating with having caries increment. The cutoff was used for classifying the caries risk level. The new assessment tool was validated in the remaining new subjects (25 %). The risk score of each individual was used to classify the caries risk and the association with having caries increment. The results of the new assessment tool for sensitivity and specificity were 66.7 and 84.6, respectively. The predictive power of the tool was 151.3. From the findings, it can be concluded that the new assessment tool had acceptable predictive power. The tool can be easily used with no additional test required, which is appropriate in a limited resources context.
1
Page : 1-9Title : Tissue Engineering: A New Paradigm for Periodontal Treatment
Author(s) : Supreda Srithanyarat
Keyword(s) : Periodontal disease,Periodontal regeneration,Stem cell,Tissue engineering
Manuscript Type : Review Article (บทความปริทัศน์)
Page : 1-9
The goal of periodontal therapy is to regenerate the previously deprived periodontal tissue caused by the periodontal infection, in order to gain the new attachment and restore its function in a healthy condition. Tissue engineering has become of interest in the field of periodontal regeneration by which its idea to reconstruct previously lost organs and tissue function, with a biocompatibility and low immune rejection. This review article aimed to update and review the previously published literatures regarding periodontal tissue engineering and to enhance the knowledge on the basis of tissue engineering. The factors influencing the successful outcome of the periodontal tissue engineering, including cells, signaling molecules and scaffolds were described and discussed. Moreover, the recent perspectives of periodontal tissue engineering technology were also introduced. Together with the knowledge of tissue engineering and profound understanding in the nature of periodontal tissue will lead to the future insightful research works and finally come across with the novel applications for periodontal therapy in the real clinical settings.
2
Page : 10-18Title : The Development of Nasal Stents “Nasoform” to Improve the Surgical Outcomes of Primary Cleft lip-nose Correction in A Patient with Unilateral Complete Cleft Lip and Palate: A Case Report
Author(s) : Panarat Kodkeaw, Krit Khwanngern
Keyword(s) : Nasal stent,Nasoform,Collapsed nose,Cleft lip
Manuscript Type : Case Report
Page : 10-18
This report presents the development of nasal stent “Nasoform” to improve the surgical outcomes of primary cleft lip-nose correction. The design of appliances that leads to the successful usage was a result of knowledge integration among the physician and the parent. This case demonstrates the benefit of using Nasoform in a patient with unilateral complete cleft lip and palate. The symmetry of nose was maintained during the healing process and during growth. The collapsed nostril was dilated and shaped to the natural form.
3
Page : 19-28Title : Oral Health Status and Relationship between Oral Hygiene Care and Remaining Natural Tooth Status of Homebound Elderly
Author(s) : Angkana Thearmontree, Mananya Roysakul, Samerchit Pithpornchaiyakul
Keyword(s) : Home bound elderly,Oral health status,Oral hygiene care,Plaque level,Tongue coating
Manuscript Type : Original Article (บทวิทยาการ)
Page : 19-28
This study was a cross-sectional analytical study. The purposes were to study the oral health status, oral hygiene care as well as the association between oral hygiene care and the remaining natural tooth status in homebound elderly. The sample consisted of 110 homebound elderly (Barthel ADL 5 - 11 or ≥12 with limited movement) aged 60 years and over, lived in Hat Yai municipality, Songkhla province. The data were obtained via interviewing and oral examination. Statistical analysis included mean, frequency, Chi-square and Fisher’s exact test. The results showedThe average age was 76.6±9.3 years ranged from 60 to 102 years old. The results showed that 75.5 % of the samples had natural teeth with an average of 11.7±10.4 teeth/person, 35.5 % had occluded teeth at least 4 pairs. About 65 % of them had the site with the highest plaque level covered more than 2/3 of tooth surface and nearly 60% had the area with highest tongue coating level of 3 (heavy coating). The study found that remaining natural tooth status was significantly associated with oral hygiene cares on tooth/gum brushing, oral cleaning frequency and appropriate oral cleaning (p<0.05). From the study are concluded High proportion of this homebound elderly had concerned oral health problems and poor oral hygiene. In addition, remaining natural tooth status was associated with oral hygiene care of the elderly.
4
Page : 29-37Title : Disto-inclined Mandibular Second Molars and Adjacent First Molars: A Study of Crown and Root Position, Morphologic features Via Panoramic Radiograph
Author(s) : Noppadol Chanpongsaeng
Keyword(s) : Disto-inclined,Mandibular second molar,Mandibular first molar,Interradicular space,Root curvature,Root proximity
Manuscript Type : Original Article (บทวิทยาการ)
Page : 29-37
The objectives of this study were to evaluate the prevalence and location of root proximity between disto-inclined mandibular second molars (7D) and adjacent first molars (6D), to examine the occlusal inclination and root curvature of 7D and 6D, compared with their normal counterparts (7N, 6N), to compare the interradicular space between 7D:6D and 7N:6N, and to evaluate the relationship between occlusal inclination and root curvature of 7D. 70 digital panoramic radiographs were studied. Image J software was used to measure occlusal inclination, root curvature at middle third and apical third of mesial and distal roots, and interradicular space of 7D:6D and 7N:6N. Paired t-tests and Pearson’s correlation analysis were used to compare differences between sides and to examine the relationship between variables, respectively. Root proximity was found in 62 from 70patients (88.57 %). Statistical significant differences of the occlusal inclination between 7D and 7N was found (mean difference = 13.50°; P<0.05). A similar finding was observed between 6D and 6N (mean difference = 1.61°; P<0.05). In 7D, apical third of both roots significantly curved distally (P<0.05). No association between occlusal inclination and root curvature of 7D was found. In conclusion, the findings of this study suggested that when 2nd molars are disto-inclined, distally curved roots of the 2nd molar, shifted occlusal inclination of both 1st and 2nd molars and root proximity between them may be expected. Early diagnosis and treatment may be advantageous in the prevention of root curvature and proximity problems.
5
Page : 38-45Title : Effectiveness of Mouth Rinse Containing Essential Oil to Reduce Plaque Level in Visual Impairment Children: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Author(s) : Arisa Srikong, Samerchit Pithpornchaiyakul
Keyword(s) : Essential oil mouth rinse,Visually impaired children,Plaque
Manuscript Type : Original Article (บทวิทยาการ)
Page : 38-45
The aim of this study was to compare the effects of an essential oil mouth rinse and placebo (220 ppm sodium fluoride mouth rinse) on plaque. This study design was a double-blind cross-over randomized control trial. Sixty-five visually impaired children that older than 8 years old were recruited and rinsed daily with 20 cc of either an essential oil or placebo under the supervision of teachers after tooth brushing before bedtime for 3 months. Interviewed questionnaire, brushing observation and plaque index were used for data collected. Percentage, mean, Chi-square and Sample t-test analysis were used for analytical comparison. The findings revealed that essential oil mouth rinse was significant in reducing plaque to score 0-2 (P-value <0.001) better than control. Using paired t-test, mean plaque of essential oil group is better than control (P-value = 0.015). Moreover, essential oil mouth rinse group had a significant reduction of plaque score 3 at baseline better than the control group (P-value = 0.005). This 3-month randomized control study demonstrated the effect of essential oil mouth rinse on plaque reduction.
6
Page : 46-52Title : Prevalence and Associated Factors of Musculoskeletal Symptoms in the Neck, Shoulder, Hands and Wrists among Thai Endodontists
Author(s) : Uraiwan Chokchanachaisakul, Jiratchaya Satitpittakul, Prawit Janwantanakul
Keyword(s) : Endodontist,Magnification,Musculoskeletal disorders,Occupational disease
Manuscript Type : Original Article (บทวิทยาการ)
Page : 46-52
The aims of this study are to investigate self-reported prevalence of musculoskeletal symptoms and the association between prevalence of musculoskeletal symptoms with certain individuals, work-related physical and
psychosocial factors among Thai endodontists. A questionnaire was mailed to 232 Thai endodontists. The questionnaire consists of four parts include personal data, professional data, musculoskeletal data and psychosocial factors. Data were analysed using chi-square, Mann-Whitney U test and logistic regression at a significant level of P<0.05. A total of 200 participants returned questionnaires at an 86 % response rate. After excluding the samples who work as an endodontists for less than 50 %, 84.9 % of Thai endodontists reported at least one musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs). The prevalence of disorders was highest in the neck (55 %) and right shoulder (48 %). Being less than 35 years old (P=0.005), having less than 5 years of work experience (P=0.001) and having a high physically demanding job (P=0.047) were factors associated with MSDs complaint. Having a previous history of symptoms (OR:2.230, 95%CI:1.06-4.70) and not being in a regularly straight back position (OR:2.629, 95%CI:1.206-5.731) had a significant correlation with present neck pain. The group of endodontists that use magnification had less prevalence of MSDs. In conclusion, a high prevalence of Thai endodontists that reported MSDs were associated with young endodontists and having a highly physically demanding job. The most prevalent region is neck pain, related with previous symptoms and awkward posture. Interventions aimed at reducing the MSDs occurrence in endodontists should focus on younger endodontists to prevent pre-symptoms and to decrease the prevalence of disorders.
7
Page : 53-59Title : Effect of Bleaching Methods on Resin Impregnated Tooth
Author(s) : Chaiwat Maneenut, Dusit Nantanapiboon
Keyword(s) : Color,Resin impregnated tooth,Tooth bleaching
Manuscript Type : Original Article (บทวิทยาการ)
Page : 53-59
The purpose of this research was to investigate the effect of bleaching methods on teeth that have a resin impregnated layer. Half of the buccal of 40 extracted maxillary premolars were luted with orthodontic resin
cement and smooth polished with a tungsten carbide bur. The other half was used as a control group. The initial color difference between both halves was unnoticed (ΔE<3). Teeth were divided into the following four groups: 1) bleached with 10 % carbamide peroxide for 8 hours per day; 2) bleached with 20 % carbamide peroxide for 8 hours per day; 3) in-office-bleaching with 40 % hydrogen peroxide every 6 days, and 4) in-office-bleaching with 40 % hydrogen peroxide (1 day) followed by 10 % carbamide peroxide for 8 hours per day. The difference of color (ΔE) between the cemented site and the controlled site was evaluated every three days using VITA Easyshade®V. The bleaching procedures were continued until the ΔE less than 3. On day 3 of bleaching, the difference of color between resin impregnated area and controlled area obviously increased in all the groups (ΔE>3). Group 3 showed the highest color contrast followed by groups 2, 4 and 1 respectively. At day 6, the only increase in contrast was with group 1 while the other group decreased. The unnoticeable color difference (ΔE<3) of group 3 was at day 6, of group 4 and 2 were at day 9 and of group 1 was at day 15. All bleaching methods created color-mismatch. A high concentration of bleaching gel caused a high contrast. However, it could reduce the contrast faster.
8
Page : 60-69Title : The Effect of Toothpaste Containing Bioactive Glass Treatment on Surface Staining Susceptibility of Bleached Teeth (In Vitro Study)
Author(s) : Thanasak Rakmanee, Chaiwat Maneenut
Keyword(s) : Bioactive glasses,Novamin,Red wine staining,Remineralizing agents,Vital tooth bleaching
Manuscript Type : Original Article (บทวิทยาการ)
Page : 60-69
The present study investigated the effects on enamel of a toothpaste containing bioactive glasses added at different time periods of in-office bleaching with 40 % hydrogen peroxide (HP) gel by evaluating the effectiveness
of bleaching and staining susceptibility, using a spectrophotometer, non-contact profilometer and scanning electron microscope (SEM). At baseline, luminosity (L1) and surface roughness (Ra0) of enamel were measured. Samples (n=48) were allocated into four groups according to the treatments: 1) bleached with 40 % HP gel (Control); 2) applied toothpaste containing bioactive glasses for 5 min prior to bleaching with 40 % HP gel (Bio_Bleach); 3) bleached with a mixture of 40 % HP gel and the toothpaste in a 1:1 proportion (Mix); 4) bleached with 40 % HP gel and immediately applied the toothpaste for 5 min (Bleach_Bio). After treatment, luminosity (L2) and roughness (Ra1) measurements and also SEM examination were performed. Samples were immersed in the staining solution (red wine) every day for 14 days. Luminosity was measured on day 7 (L3) and day 14 (L4). At baseline, L1 values of all groups were not significantly different. After bleaching, L values (L2) in all groups increased significantly and Mix group significantly showed the lowest L values comparing to the others. After 7-day staining, L values (L3) in all groups decreased but only the control and Bio_Bleach groups showed significant differences compared to the after bleached values. After 14 days of staining, all groups, except the Mix group, significantly demonstrated lower L values relatively to the values at 7-day staining. Despite the fact that surface roughness in all groups increased after the completion of the bleaching process, only Bio_Bleach and Bleach_Bio groups were statistically significant relatively to the baseline. SEM analysis presented morphological alterations characterized by depressions, porosities and superficial irregularities in different degrees. A treated enamel surface with toothpaste containing bioactive glass either during or after 40 % HP in-office bleaching process reduced red wine staining.
9
Page : 70-82Title : Effect of Primary School-Based Oral Health Program and Oral Behaviors on Dental Caries among 12- and 15-Year-Old Children
Author(s) : Narisa Klinkhiaw, Songchai Thitasomakul, Supatcharin Piwat, Oitip Chankanka, Sukanya Tianviwat
Keyword(s) : Caries increment,School-based oral health program,Oral health behaviors
Manuscript Type : Original Article (บทวิทยาการ)
Page : 70-82
The objectives of this study were to explore the caries prevalence of 8-, 12- and 15-year-old children and the effect of school-based oral health program, knowledge, attitude and oral behaviors on caries increment of children from 8 to 12 and from 12 to 15 years. A longitudinal study was conducted in 704 children aged 8, 12 and 15 years old in Thepha district, Songkhla province. Children were oral examined, follow up changes in oral health status and oral health behaviors. Data were analyzed and presented in percentage and mean. Logistic regression was used to identify risk factors of caries increment. The results show that caries prevalence was 72.4 % in 8 years old and increased to 92.5 % and 97.1 % in 12 and 15 years old children given the DMFT-8 year, DMFT-12 year and DMFT-15 year of 1.7±1.5, 5.0±3.5 and 8.4±4.5, respectively. Caries increment was 7.2±6.5 surfaces/person in the period from 8 to 12 years and increased to 8.6±6.4 surfaces/person in the period from 12 to 15 years. More than 60 % of the children had sealant, Brushing system at school—brushing together after lunch, opening the music while brushing, teacher or student leader-supervised brushing and checking oral cleanliness after brushing—was seldom. Logistic regression analysis showed a statistically significant association between the caries increment8-12 with none sealant (ORadj = 1.517, 95%CI = 1.052-2.187). The caries increment12-15 associated with poor oral cleanliness (ORadj = 2.002, 95%CI = 1.296-3.093) and none sealant (ORadj = 1.888, 95%CI = 1.217-2.930). In conclusion, children in Thepha district had high level and increased by age of caries prevalence, caries severity and caries increment. Promoting in oral cleanliness and sealant led to reduction of caries increment in children.
10
Page : 83-91Title : Effect of Storage Temperatures on the Shear Bond Strength of Three Resin Cements to Dentin
Author(s) : Tool Sriamporn, Kanjana Sansaneeyawat, Awiruth Klaisiri, Niyom Thamrongananskul
Keyword(s) : Degradation,Resin cement,Shear bond strength,Storage temperature
Manuscript Type : Original Article (บทวิทยาการ)
Page : 83-91
The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of storage temperature on the shear bond strengths of three resin cements to dentin. Ninety extracted human permanent molars were cut to flat expose dentin surface.
The specimens were randomly divided into three groups (n=30) based on the storage temperature of the selected resin cement (4, 25, and 40 oC). Each group was then subdivided into three subgroups based on the type of resin cement used (Variolink N, Panavia F 2.0 and RelyX U200). Resin composite blocks were bonded onto each specimen using the specified cement from its group. Subsequently, all samples were immersed in 37 oC distilled water for 24 hours. Shear bond strength testing was performed using a universal testing machine at a cross head speed of 0.5 mm/minute. Data was statistically analyzed by Two-way ANOVA and Turkey’s multiple comparison tests at a 95 % confidence level. Furthermore, the modes of failure were examined under a stereomicroscope at 40x magnification. Results showed that there were no statistically significant differences in shear bond strength between Variolink N and Panavia F 2.0 stored at 4 or 25 oC. The shear bond strengths of these groups were significantly higher than other experimental groups. Resin cements stored at 40oC produced significantly lower shear bond strengths than those stored at 4 and 25 oC (p>0.05). RelyX U200 stored at 40oC demonstrated the lowest shear bond strength, with values significantly lower than all other groups. All Variolink N and Panavia F 2.0 specimens exhibited mixed failures, whereas all RelyX U200 specimens demonstrated adhesive failure. In conclusion, storing resin cement at 40oC for three months may significantly lower shear bond strength when bonded to the dentin compared to those that were stored at the temperature of 4 and 25 oC.
11
Page : 92-100Title : Fracture Resistance of Occlusal Ceramic and Composite Molar Onlay Comparing to Lithium Disilicate Molar Crown
Author(s) : Chalermpol Leevailoj, Jatuporn Luekiatpaisarn
Keyword(s) : CAD/CAM,Lithium-disilicate ceramic,Polymer-infiltrated ceramic network,Thin occlusal onlay
Manuscript Type : Original Article (บทวิทยาการ)
Page : 92-100
This in vitro study aimed to evaluate fracture strength and failure modes of thin occlusal onlays fabricated from direct resin composite, CAD/CAM polymer-infiltrated ceramic-network/hybrid ceramic, and CAD/CAM lithiumdisilicate glass ceramic under compressive loading. Forty extracted maxillary molars were prepared, including occlusal enamel and dentin removal, leaving two dentin slopes with peripheral enamel. Thirty teeth were restored with 0.6-mm-thick occlusal onlays using direct resin composite (Premise), CAD/CAM polymer-infiltrated ceramic-network/hybrid ceramic (Vita Enamic), and CAD/CAM lithium-disilicate glass ceramic (IPS e.max CAD). Others were restored with IPS e.max CAD crowns (n=10). The milled restorations were luted with adhesive resin cement. All restored teeth were loaded vertically by means of a universal testing machine. Fracture loading data were recorded in Newtons (N) and statistically analyzed. The failure modes were classified, and correlations between fracture strength and failure mode were analyzed. The fracture strengths (mean±SD) were ranging from 1,949.59 to 2,870.44 N. The IPS e.max CAD onlays showed significantly higher fracture strength than the IPS e.max CAD crowns (p<0.05). There was no correlation between fracture strength and failure modes found within each material. In conclusion, the fracture strength of the Vita Enamic occlusal onlay was comparable with that of the Premise occlusal onlay and the IPS e.max CAD onlay. The IPS e.max CAD onlay provided higher fracture resistance than the IPS e.max CAD crown. However, all restorations demonstrated higher fracture resistance than that required for the average force of mastication.
12
Page : 101-109Title : Comparison Video Based Learning Versus Live Demonstration of Dental Student Knowledge and Skills for Working Length Determination Using Electronic Apex Locator
Author(s) : Thanomsuk Jearanaiphaisarn, Paweena Hanuksornnarong
Keyword(s) : Dental student,Live Demonstration,Self-directed learning,Video Based Learning
Manuscript Type : Original Article (บทวิทยาการ)
Page : 101-109
The objectives of this study were to compare the effectiveness of video based learning (Video) versus a live demonstration (Demo) on dental student knowledge and skills for working length determination with electronic apex locator and to evaluate their improvement after self-directed video based learning. Sixty-three dental students were randomly assigned to two teaching groups. In the classroom, the Demo group attended a live demonstration and the Video group watched a video about working length determination with electronic apex locator. The knowledge and skills were evaluated by using multiple choice questions and a practical test. After all the students had self-studied an online video for 6 weeks, the second practical test was performed. Satisfaction questionnaires were completed after each practical test. The Mann–Whitney U test and the Wilcoxon signed-ranks test were used to compare the scores between groups and within group, respectively. There were no significant differences in knowledge or practical scores between the Demo and Video groups. After self-directed learning, the Video group practical score significantly increased, however, no differences were found in the Demo group. The Demo group was significantly more satisfied with their learning method. In conclusion, video based learning enhanced the knowledge and skills of dental students for working length determination with electronic apex locator as well as a live demonstration had done. Self-directed video based learning subsequent to classroom video improved practical skills.